-
Your shopping cart is empty!






- Stock: In Stock
- Package: 50 MCG/TAB / 100 TABS
Ask a Question About This Product
- Active ingredient: Levothyroxine Sodium (T4)
- Type: Tyroid
- Form: Oral (pills)
Description
Levothyroxine is a synthetic form of thyroxine (T4), an endogenous hormone secreted by the thyroid gland, which is converted to its active metabolite, L-triiodothyronine (T3). T4 and T3 bind to thyroid receptor proteins in the cell nucleus and cause metabolic effects through the control of DNA transcription and protein synthesis. Like its naturally secreted counterpart, levothyroxine is a chiral compound in the L-form.
Purposes of use
Levothyroxine is a drug that is used to treat underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) and other conditions when a person's thyroid hormone production is below normal. Levothyroxine sodium replaces or provides thyroid hormone support, which is normally produced by the thyroid gland. Low thyroid hormone levels can occur naturally or when the thyroid gland is injured by radiation/medications or removed by surgery. Levothyroxine is also known as L-thyroxine or T4.
Enhanced Metabolism
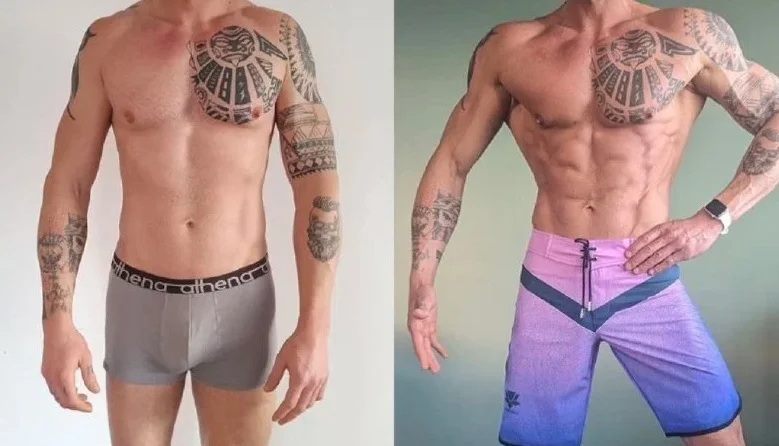
By normalizing thyroid function, Levothyroxine Sodium helps maintain a healthy metabolism, which is crucial for effective fat loss and muscle gain phases. Increased Energy Levels Proper thyroid function can lead to better energy levels, ensuring you have the stamina and endurance needed for rigorous training sessions.
Improved Muscle Recovery
Balanced thyroid hormones can aid in protein synthesis and muscle repair, crucial for bodybuilders in their recovery phase.
Weight Management
By regulating the metabolism, this medication assists in maintaining a healthy weight, a key factor in bodybuilding for both aesthetic and performance goals. Consistent Performance Stable thyroid levels ensure consistent physical and mental performance, crucial for athletes who need to maintain a high level of training intensity.
Use with Growth hormone
Patients, receiving Human Growth Hormone (HGH) should take T4 to prevent the lack of this hormone, as growth hormone significantly increase T4 to T3 conversion, which can cause pathologic T4 deficiency.
Dosage and administration
It is recommended that levothyroxine be taken with an empty stomach approximately half an hour to an hour before meals to maximize its absorption. It is also recommended that the patient take the tablet with one glass of water to ease swallowing as well as to help the tablet dissolve for absorption. Dosages vary according the age groups and the individual condition of the patient, body weight and compliance to the medication and diet. Maximum dosage may reach 300-400 mcg per day but that is rare. Most people need to be careful to start with a low dosage and consult with a doctor to define the optimal dose.
How to use
Basically, the dosage starts with 25-50 mcg per day and every 5-6 days increases by 25-50 mcg per day. And the maximum is 300-400 mcg per day. Distribute a few tablets throughout the day. The maximum cycle lasts seven weeks. At least six weeks should pass between cycles. In addition, it will return your thyroid gland to normal functioning. It is commonly stacked with clenbutos to make both even more effective at burning fat.
- Average dose: 100 to 200 mcg per day
- Effective dosage: pyramidal method Proven cycle: 5-6 weeks
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption of orally administered levothyroxine ranges from 40 to 80%, with the majority of the drug absorbed from the jejunum and upper ileum. Levothyroxine absorption is increased by fasting and decreased in certain syndromes, by certain foods, and with age.
Half-life elimination is 6–7 days for people with normal lab results; 9–10 days for people with hypothyroidism; 3–4 days for people with hyperthyroidism. Thyroid hormones are primarily eliminated by the kidneys (approximately 80%), with urinary excretion decreasing with age. The remaining 20% of T4 eliminated in the stool.
Effects
- Regulates your metabolism
- Burns fat
- Increase anabolic processes and muscle growth
- Central nervous system stimulation
Side effects
Allergies to the medicine are unlikely, but if the patient develops a severe reaction to this drug such as difficulty breathing, shortness of breath or swelling of the face and tongue it is imperative that the patient immediately seek medical attention. Adverse events are generally caused by incorrect dosing. Side effects from excessive doses include weight loss, trouble tolerating heat, sweating, anxiety, trouble sleeping, tremor, and fast heart rate. Use is not recommended in people who have had a recent heart attack. Use during pregnancy has been found to be safe. Acute overdose may cause fever, hypoglycemia, heart failure, coma and unrecognized adrenal insufficiency. Acute massive overdose may be life-threatening; treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. Massive overdose may be a require beta-blockers for increased sympathomimetic activity. The side effects of overdosing appear 6 hours to 11 days after ingestion.
- Chest pain, discomfort, or tightness
- Difficulty with swallowing
- Extreme fatigue
- Fainting Fast, slow, irregular, pounding, or racing heartbeat or pulse
- Heat intolerance
- Nausea
- Sweating
- Tremors
Profile
- Half-life: 6-24 hours
- Frequency of intake: 1-2 times per day
Precautions
Prolonged use of high dosages may lead to serious problems with thyroid system and suppression of endogenous hormone production. Studies shows up to 20% decrease of endogenous production after 3 weeks of usage. However, when used properly at recommended dosages, thyroid function restores after 3-4 weeks Levothyroxin has adrenalin-like effects including increased heart rate and nervousness, which could be avoided by using beta-blockaders
Contraindications
Levothyroxine is contraindicated in people with hypersensitivity to levothyroxine sodium or any component of the formulation, people with acute myocardial infarction, and people with thyrotoxicosis of any etiology. Levothyroxine is also contraindicated for people with uncorrected adrenal insufficiency, as thyroid hormones may cause an acute adrenal crisis by increasing the metabolic clearance of glucocorticoids.
Drug interactions
There are also foods and other substances that can interfere with absorption of thyroxine replacement. Avoid taking calcium and iron supplements within 4 hours of the medication and avoid taking soy products within 3 hours of the medication as these can reduce absorption of the medication. Other substances reducing absorption are aluminium and magnesium containing antacids, simethicone or sucralfate, Cholestyramine, colestipol, Kayexalate.
Other substances cause other adverse effects that may be severe. Ketamine may cause hypertension and tachycardia and Tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants increase its toxicity. On the other hand Lithium causes hyperthyroidism by affecting iodine metabolism of the thyroid itself and thus inhibits Synthetic levothyroxine as well.
Special warnings
Levothyroxine Sodium should be introduced very gradually in patients aged over 50 years and those with long standing hypothyroidism to avoid any sudden increase in metabolic demands. Patients with panhypopituitarism or other causes predisposing to adrenal insufficiency may react to levothyroxine treatment, and it is advisable to start corticosteroid therapy before giving levothyroxine to such patients. Levothyroxine Sodium should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, including angina, coronary artery disease, hypertension, and in the elderly who have a greater likelihood of occult cardiac disease.
Contraindicated in patients with untreated subclinical (suppressed serum TSH level with normal T3 and T4 levels) overt thyrotoxicosis of any etiology and in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Thyroid replacement therapy may cause an increase in dosage requirements of insulin or other anti-diabetic therapy (such as metformin). Care is needed for patients with diabetes mellitus, and diabetes insipidus. Subclinical hyperthyroidism may be associated with bone loss. To minimise the risk of osteoporosis, dosage of levothyroxine sodium should be titrated to the lowest possible effective level.
Storage
- Keep away from children
- Keep in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight
- Store at room temperature
- Do not use after the expiry date