
- Stock: In Stock
- Package: 10ml/vial
Ask a Question About This Product

L-Carnitine is an amino acid that is produced in your body naturally, mostly in the liver and kidneys, from two amino acids called lysine and methionine. Its main job is to help move fats into mitochondria cells, where the fats get broken down to create energy, known as ATP. You can get L-Carnitine from food sources like red meat, poultry, fish, and dairy, but for many athletes and bodybuilders, relying on these dietary sources alone doesn't cut especially when trying to maximize endurance or cut fat. That's where injectable version comes in. It's absorbed directly into the bloodstream, allowing faster and more effective results compared to oral supplements.
The main difference of L-Carnitine - unlike stimulants or thermogenic agents, it doesn't rev up the nervous system or raise body temperature to aid fat loss. So, you don't get the jitters, anxiety, or a racing heart, which makes it a much easier option for people who want to steer clear of stimulant-related side effects. What it does instead is help your body use fat more effectively as energy, making things run smoother and more reliably.
In the fitness and bodybuilding world, L-Carnitine is also appreciated for how it helps with recovery. During training, L-Carnitine helps the body use glycogen more efficiently and also stimulates the use of fat as fuel. Thanks to this, athletes can train longer and more effectively without feeling severe muscle fatigue. L-Carnitine is often used during cutting phases when the main goal is to lose fat while maintaining muscle mass. L-carnitine helps maintain stable energy levels during prolonged physical activity, so athletes involved in endurance sports also benefit.
Some studies suggest that L-carnitine may be beneficial for the cardiovascular system, especially for professional athletes. L-carnitine improves the process of burning fat in heart cells as well, which helps the heart work more efficiently during intense training.
Main Effects and Benefits
- Fat Oxidation and Weight Management: L-Carnitine plays a critical role in transporting long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are oxidized for energy production. This makes it an invaluable supplement for athletes during cutting phases or for those aiming to reduce body fat while maintaining lean muscle mass. Research has shown that L-Carnitine supplementation enhances fat oxidation during exercise, making it a key factor in improving body composition for competitive athletes.
- Enhanced Endurance and Glycogen Sparing: L-Carnitine increases the use of fat as a fuel source during aerobic exercise, thereby sparing muscle glycogen stores. This "glycogen-sparing" effect delays the onset of fatigue, allowing athletes to perform for longer durations without hitting the wall. Studies confirm that athletes supplementing with L-Carnitine experience improved endurance and prolonged performance during high-intensity workouts.
- Improved Recovery and Reduced Muscle Soreness: Intense physical training leads to muscle damage and oxidative stress. L-Carnitine has been shown to reduce post-exercise muscle soreness by enhancing blood flow to muscles, improving oxygen delivery, and reducing inflammation. This accelerates recovery times and minimizes muscle damage, allowing athletes to maintain a high training frequency without prolonged downtime.
- Anaerobic Performance Boost: Although L-Carnitine is primarily known for enhancing aerobic endurance, it has been shown to improve performance in strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) as well. By reducing muscle fatigue and damage, L-Carnitine helps strength athletes complete more repetitions and sets, contributing to greater muscle gains over time.
- Cardiovascular Endurance and Protection: For endurance athletes, maintaining cardiovascular health is crucial. L-Carnitine enhances heart function by improving fat metabolism within cardiac muscle, which provides a steady source of energy for the heart during prolonged activity. This not only supports overall endurance but also helps protect the heart from exercise-induced stress, which is important for long-duration or high-intensity athletes.
- Cognitive Function and Brain Health: L-Carnitine, particularly in its acetylated form (Acetyl-L-Carnitine or ALCAR), has been shown to support cognitive function by improving mitochondrial function in brain cells and enhancing the production of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory. Athletes, especially those in mentally demanding sports, benefit from L-Carnitine’s ability to improve focus, reaction time, and mental clarity.
- Neuroprotective Effects: L-Carnitine reduces oxidative damage in neurons, which can protect against neurodegenerative conditions and mental fatigue. This makes it a valuable supplement for both younger athletes looking to optimize mental sharpness and older individuals seeking to preserve cognitive function.
- Metabolic Health and Insulin Sensitivity: L-Carnitine has been shown to improve metabolic function in overweight individuals and those with insulin resistance. By promoting the oxidation of fats, it helps reduce fat buildup in the liver and muscle tissues, which can enhance insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health. This is particularly beneficial for individuals looking to manage type 2 diabetes or prevent metabolic syndrome.
- Male Fertility Support: L-Carnitine is commonly used in fertility treatments for men due to its ability to improve sperm motility and quality. Studies have demonstrated that L-Carnitine supplementation enhances sperm maturation and energy production, making it a valuable supplement for improving reproductive health.
- Fatigue-Related Disorders and Chronic Conditions: L-Carnitine is often prescribed to individuals suffering from chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) or fibromyalgia. By improving mitochondrial efficiency and reducing oxidative stress, L-Carnitine helps alleviate symptoms of fatigue, muscle pain, and cognitive fog, making it a key supplement for patients with these conditions.
Mechanism of Action
L-Carnitine helps your body effectively use fats as a primary energy source. The main mechanism of its action is that it transports fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are converted into energy. This process consists of several stages that involve various enzymes and cellular structures, but overall, the essence is that L-Carnitine helps us burn fat faster. Below, we’ll take a closer look at the specific processes that L-Carnitine is involved in.
Transport of Long-Chain Fatty Acids into the Mitochondria
L-Carnitine helps your body burn fat by moving long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they’re turned into energy. Since these fats are too large to get into the mitochondria on their own, L-Carnitine works like a transporter, carrying them inside. The whole process happens through several steps, including getting the fatty acids ready and attaching them to L-Carnitine. Let’s break down each of these steps to see how L-Carnitine makes energy production possible:
-
Activation of Fatty Acids: Before L-Carnitine can help move fatty acids into the mitochondria, these fats need to be "activated." This happens in the cell, where long-chain fatty acids are turned into a form that’s ready to be used. This step needs some energy (ATP) to make the fats ready for transport.
- Carnitine Acyltransferase I (CPT-I): After the fatty acids are activated, they still can’t cross the mitochondrial membrane. An enzyme called CPT-I helps attach the fatty acids to L-Carnitine, forming a new molecule that’s small enough to pass through the membrane.
- Carnitine-Acylcarnitine Translocase (CACT): Once the fatty acids are attached to L-Carnitine, they are transported into the mitochondria by a protein called CACT. This protein swaps the new fatty acid molecule for a free L-Carnitine molecule, making sure the cycle keeps going.

Inside the Mitochondria: Beta-Oxidation of Fatty Acids
Once inside the mitochondria, the fatty acid is handed back to Coenzyme A (CoA) with the help of an enzyme called CPT-II. This step frees up L-Carnitine, which exits the mitochondria, while the fatty acyl-CoA is ready to be broken down.
- Beta-Oxidation: This is the process where fatty acids are broken down in the mitochondria. During beta-oxidation, fatty acids are split into smaller pieces, each with two carbon atoms. Each cycle of this process produces:
- Acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid (Krebs) cycle to create energy (ATP).
- FADH2 and NADH, which help generate even more energy through a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
- Energy Production (ATP Synthesis): The acetyl-CoA that’s made from beta-oxidation enters the citric acid cycle, where it creates more NADH and FADH2. These molecules then enter the electron transport chain, producing a lot of ATP.

This whole process is very efficient at creating energy from fat, which is why L-Carnitine plays a key role in sustaining energy levels by helping the body use fat more effectively.
Recycling of L-Carnitine
After the fatty acid has been transferred to Coenzyme A inside the mitochondria, L-Carnitine is freed up and ready to be reused. It leaves the mitochondria through the same transport protein that helped it bring the fatty acid in. This recycling process allows L-Carnitine to keep bringing more fatty acids into the mitochondria, making it a crucial part of the fat-burning process.
Prevention of Toxic Accumulation and Cellular Homeostasis
L-Carnitine has another important job—making sure toxic byproducts from fat metabolism don’t build up in the cells. If fatty acids aren’t broken down properly, they can pile up in the cell and cause problems, leading to something called lipotoxicity. By helping transport fatty acids into the mitochondria, L-Carnitine keeps these harmful byproducts from accumulating, helping cells stay balanced and healthy.
L-Carnitine also helps clear out short- and medium-chain fats that can build up in the mitochondria during metabolism. Even though these fats are smaller, they can still slow down the cell’s ability to produce energy if not dealt with. L-Carnitine binds to them and moves them out of the mitochondria, keeping everything running smoothly.

Supporting Mitochondrial Growth and Protecting Cells
L-Carnitine doesn’t just help with burning fat—it also plays a role in keeping your mitochondria healthy. By ensuring fatty acids are continuously oxidized, L-Carnitine helps mitochondria work efficiently. Some research even suggests that L-Carnitine might help create new mitochondria, which is especially important for endurance athletes since more mitochondria means better energy production and improved performance (https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052717, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.009).
On top of that, L-Carnitine acts as an antioxidant, helping to reduce oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals that are produced during intense exercise. This protective effect minimizes damage to cells, aids recovery, and helps maintain muscle health over time, boosting endurance and overall performance.
Influence on Metabolic Regulation and Exercise Performance
L-Carnitine not only boosts fat metabolism but also helps regulate overall energy use in the body. By increasing fat oxidation, it reduces the body’s dependence on glycogen, helping to conserve it. This can extend your ability to exercise, especially during endurance activities. During long aerobic workouts, this shift allows athletes to keep performing without reaching the point of extreme fatigue, often referred to as hitting the "wall," which happens when glycogen levels are depleted.
- Glycogen Sparing: L-Carnitine encourages the body to use fat as the main energy source, saving muscle glycogen for when it’s really needed. This is particularly useful for athletes during long or intense activities where glycogen is vital for maintaining energy levels.
- Enhanced Recovery: L-Carnitine also helps you recover faster after exercise by reducing muscle damage and clearing out waste products like lactic acid. This speeds up muscle repair and reduces soreness, allowing you to get back to training sooner and at full capacity.
The image above illustrates how L-Carnitine supports glycogen sparing by promoting fat as the primary energy source, which helps maintain endurance and delay fatigue.
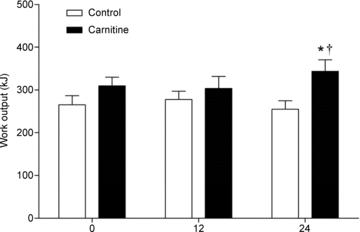
A study looked into the effects of long-term carnitine supplementation (2g twice daily with carbohydrates) on metabolism and endurance performance during exercise. Over six months, subjects exercised at both low and high intensities. L-Carnitine increased fat oxidation and conserved glycogen at lower intensities, while at higher intensities, it reduced the buildup of waste products, allowing for more efficient use of carbohydrates. As a result, the participants achieved higher work output during a 30-minute time trial (https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2010.201343).
Broad Impact on Health Beyond Energy Production
L-Carnitine does more than just help with fat metabolism—it also has wider health benefits. For heart health, it helps the heart muscle use fats more efficiently, which improves how the heart works and may lower the risk of cardiovascular disease. L-Carnitine also supports brain health by boosting energy production in brain cells, which could help reduce the risk of neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s (https://doi.org/10.1097/00004850-200303000-00001).
Uses
L-Carnitine, in all its forms—whether oral, injectable, or transdermal—has broad applications across both clinical and athletic settings. It is a versatile nutrient that supports fat metabolism, energy production, cardiovascular health, and even cognitive function. Below is an in-depth look at how L-Carnitine is used in different forms and for various purposes beyond the injectable format.
Fat Loss and Body Composition
L-Carnitine is a go-to supplement for those looking to burn fat and improve their body composition, whether they’re athletes or just trying to get in shape. It works by helping to transport fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they’re burned for energy, especially during exercise. When combined with a diet that's lower in calories, this process helps with fat loss while also protecting muscle mass. Studies have also found that L-Carnitine can boost overall metabolic health, particularly for people who are overweight or obese, by reducing body fat and improving things like insulin sensitivity (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.03.008).

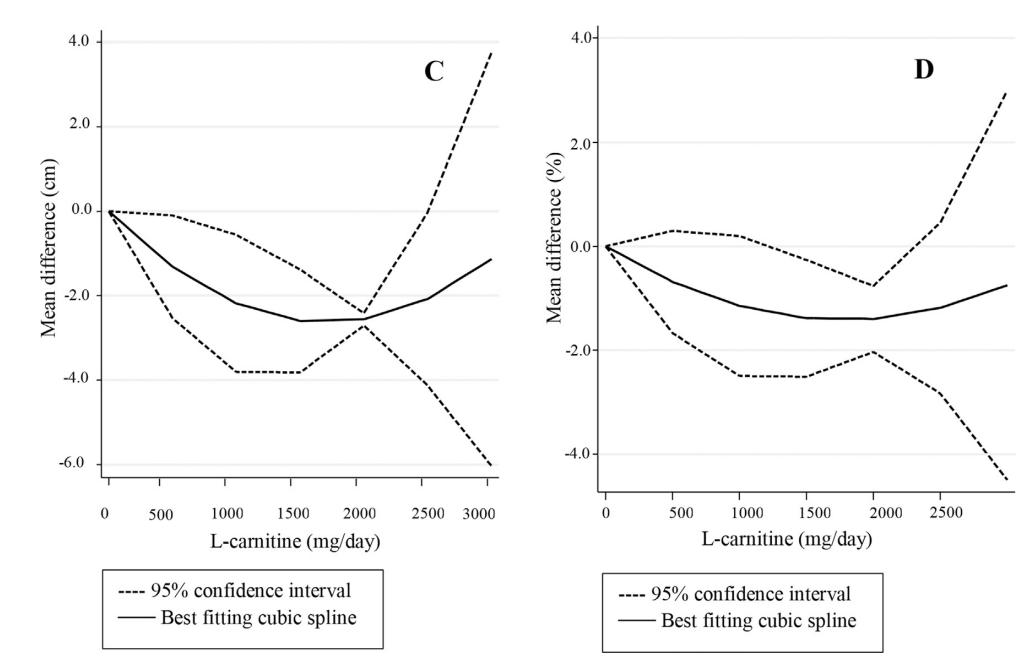
In the graphs above:
- Body weight (A): Increasing L-Carnitine intake to around 2000 mg/day is linked with a notable reduction in body weight (about 1.5 kg), after which the effect levels out.
- BMI (B): Although changes in BMI aren’t as dramatic, there is a slight decrease around the same 2000 mg/day dosage.
- Waist circumference (C): L-Carnitine also helps reduce waist size, with a significant decrease (around 4 cm) at doses up to 2000 mg/day, before the effect stabilizes.
- Body fat percentage (D): Similarly, body fat percentage drops significantly up to 2000 mg/day, after which further reductions taper off.
Enhancing Athletic Performance and Endurance
Many athletes use L-Carnitine to help with both endurance and strength training. It supports fat burning and energy production, which means better stamina, less muscle soreness, and faster recovery after hard workouts. This applies whether you take L-Carnitine as a supplement or use it on your skin.
- Better Endurance for Aerobic Activities: L-Carnitine helps your body switch from burning glycogen to burning fat for energy, allowing you to keep going longer without getting tired. Research has shown that L-Carnitine supplements can really help with endurance, especially for activities like running and cycling (https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2010.201343).

- Better Performance in Strength Training: For those focused on lifting weights or resistance training, L-Carnitine can also be a great tool. It helps muscles recover faster and reduces damage, allowing you to train harder and improve your results over time. This is particularly useful if you’re looking for a performance boost during strength sessions (https://doi.org/10.20463/jenb.2018.0026).

The graphs above illustrate the changes in strength (repetitions and lifting volume) for the bench press (BP) and leg press (LP) exercises, comparing two groups: one that took a placebo (PLA) and another that took L-Carnitine (LCR). Measurements were taken at weeks 3, 6, and 9:
- A (BP repetitions): The group taking L-Carnitine showed an increase in the number of repetitions compared to the placebo group at all time points, with significant improvements at weeks 6 and 9.
- B (BP lifting volume): The L-Carnitine group also lifted more total weight, with a particularly notable increase by week 9, where the difference became statistically significant.
- C (LP repetitions): For leg press, the L-Carnitine group saw a significant increase in repetitions at weeks 6 and 9 compared to the placebo group.
- D (LP lifting volume): The total lifting volume for the leg press increased significantly in the L-Carnitine group from week 6 onwards and stayed higher at week 9.
Recovery and Muscle Soreness Reduction
L-Carnitine has been proven to speed up recovery after tough workouts, whether you're doing cardio or strength training. It works by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in your muscles, which helps you bounce back faster and keep training hard without needing as much downtime.
- Reducing Muscle Soreness and Damage: A study from the American Journal of Physiology showed that athletes doing high-intensity interval training had less muscle soreness and damage when they took L-Carnitine. This is likely because L-Carnitine improves blood flow to your muscles and helps clear out waste products like lactic acid faster, which can otherwise lead to soreness.
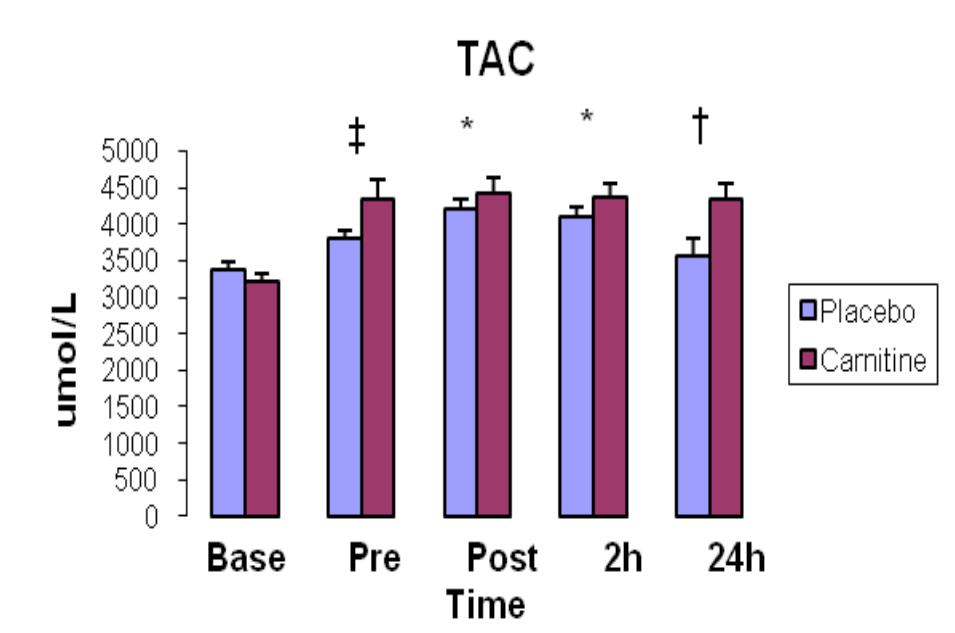
The graph above shows the total antioxidant capacity (TAC) in the blood of people who took L-Carnitine versus those who took a placebo, measured at different times:
- Baseline (Base): Both groups started with similar TAC levels.
- Before exercise (Pre): The L-Carnitine group already had a significantly higher TAC level compared to the placebo group (marked by ‡).
- After exercise (Post) and 2 hours later (2h): The L-Carnitine group continued to show much higher TAC levels than the placebo group (marked by *).
- 24 hours later (24h): Even 24 hours after exercising, the L-Carnitine group had higher TAC levels compared to the placebo group (marked by †).
Conclusion: Taking L-Carnitine can significantly boost your body’s antioxidant capacity both before and after working out, with benefits lasting up to 24 hours. This enhanced protection might help reduce the oxidative stress caused by exercise (https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-13-79).
Cardiovascular Health and Function
L-Carnitine is often used in clinical settings to support heart health. Its ability to boost fat metabolism in heart tissue makes it an important supplement for improving heart function, especially in people with cardiovascular disease or those at risk. This benefit isn’t limited to clinical patients—it’s also helpful for athletes.
- Supporting Heart Health and Fat Metabolism: L-Carnitine helps the heart burn fat more efficiently, giving it a steady supply of energy, especially during exercise. A study published in Circulation found that L-Carnitine supplementation improved how well the heart works, increased exercise tolerance, and reduced symptoms in people with heart disease (https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.1055-18).
- Reducing Exercise-Induced Heart Stress: For athletes, L-Carnitine also plays a role in protecting the heart during high-intensity exercise. It reduces oxidative stress, helping the heart perform better even under tough conditions. Research has shown that athletes who take L-Carnitine have lower levels of markers associated with heart stress after intense workouts (https://doi.org/10.20463/jenb.2018.0026).
Cognitive Function and Neuroprotection
L-Carnitine, especially in its acetylated form (Acetyl-L-Carnitine or ALCAR), is known for giving your brain a boost. While ALCAR tends to get more attention for its cognitive benefits, regular L-Carnitine can also help protect brain cells by improving how your mitochondria work—those little powerhouses in your cells that keep everything running smoothly.
- Memory and Focus: Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR) can cross into the brain and helps your body make acetylcholine, which is key for memory and learning. Studies show ALCAR can sharpen your focus, improve attention, and even give you a mental clarity boost, especially if you’re stressed or getting older. It helps brain cells produce more energy, which keeps your mind alert and your memory strong (https://doi.org/10.1007/s44192-023-00056-z).
- Protecting Your Brain: ALCAR also works like a shield for your brain. It reduces oxidative stress—basically, it helps prevent the kind of damage that can slow down your brain over time. Plus, it supports brain cells by keeping their energy levels up, making sure they stay healthy. Athletes often use ALCAR for mental sharpness, but it’s also great for keeping your brain in top shape as you age (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2288-7).
Support in Metabolic and Fatigue-Related Disorders
L-Carnitine is often recommended by doctors to help with metabolic issues, especially those linked to problems with mitochondrial function or chronic fatigue. It’s commonly used for conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), fibromyalgia, and even certain mitochondrial diseases.
- Helping with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS): Research has shown that L-Carnitine can improve how mitochondria work, which helps reduce fatigue in people with CFS. A study published in Neuropsychobiology found that after 8 weeks of taking L-Carnitine, patients noticed big improvements in their fatigue levels, especially between weeks 4 and 8. It’s a safe, well-tolerated treatment that can boost overall energy and improve quality of life for people with CFS. You can check out the study here: https://doi.org/10.1159/000119325.
- Improving Metabolic Health in Diabetics: L-Carnitine is also used to help people with type 2 diabetes. It’s been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the buildup of harmful fats in tissues. A study in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition found that L-Carnitine supplementation helped improve how the body processes glucose and reduced fat buildup in diabetic patients. You can read more about the study here: https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.1999.10718830.
Male Fertility Support
L-Carnitine is often used in treatments to support male fertility. It’s been shown to improve sperm quality by boosting energy production in sperm cells and reducing oxidative stress—two key factors for reproductive health.
- Improving Sperm Motility and Count: Research has found that even taking as little as 2 grams of L-Carnitine per day can help improve sperm motility, increase sperm count, and boost overall fertility. It does this by helping regulate hormone levels and reducing the effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can cause damage. L-Carnitine also plays a role in the development of germ cells by influencing Sertoli cells. While the exact details are still being studied, there’s strong evidence that L-Carnitine can have a positive impact on male fertility. You can read more about the research here: https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185796.

L-Carnitine in Elderly Populations
L-Carnitine is often used to support energy production and improve mitochondrial function in older adults. It helps combat the natural decline in physical and cognitive abilities that comes with aging.
- Preserving Muscle Mass in Older Adults: Research shows that L-Carnitine can help fight sarcopenia, which is the loss of muscle mass as we age. A study published in Nutrition & Metabolism found that older adults who took a combination of L-Carnitine, leucine, and creatine saw significant improvements in muscle strength and lean body mass after just 8 weeks. This suggests that L-Carnitine can play a key role in preventing muscle breakdown and improving physical performance in older people. You can check out the study here: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-016-0158-y.
- Supporting Cognitive Health in Aging: Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR) is well-known for its cognitive benefits, especially in older adults. It can cross into the brain and boost mitochondrial function, which helps reduce oxidative stress in brain cells. This supports better memory, learning, and overall mental clarity. Studies show that ALCAR is particularly effective in improving cognitive function in older adults dealing with age-related decline. More information can be found here: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051389.
Differences Between Oral and Injectable L-Carnitine
L-Carnitine is well-known for helping with fat metabolism and energy production, and it comes in both oral and injectable forms. While both can boost fat burning and improve endurance, there are some key differences when it comes to how they’re absorbed, their bioavailability, and how effective they are, which can affect how they’re used.
- Bioavailability and Absorption Rates: One of the biggest differences between oral and injectable L-Carnitine is how much of it your body actually absorbs. With oral L-Carnitine, only about 15-18% of what you take makes it into your bloodstream because of what’s called "first-pass metabolism" in your liver and digestive system. This means a lot of it doesn’t get used efficiently, so you may need to take higher doses to see the results you want. Injectable L-Carnitine, on the other hand, skips the digestive system entirely and goes straight into your bloodstream, giving you almost 100% absorption. This makes the injectable form much more potent and effective, so you can take lower doses and still see significant effects.
- Onset of Action: Because injectable L-Carnitine goes directly into your bloodstream, it starts working much faster than the oral form. You can feel the effects within minutes after injection, which is especially useful when you need quick results, like during intense workouts or fat-loss phases. Oral L-Carnitine takes longer to kick in—plasma levels don’t peak until a few hours after you take it.
- Side Effects and Tolerability: Oral L-Carnitine can sometimes cause mild digestive issues like nausea or diarrhea, especially if you’re taking higher doses. Injectable L-Carnitine avoids these problems since it bypasses your digestive system altogether. However, there is a chance of local irritation or pain at the injection site if it’s not administered properly.
Dosage, Administration, and Precautions
- Dosage: For injectable L-Carnitine, most people take between 500 mg and 2,000 mg a day, depending on their goals and body weight. If you’re an athlete, you might tweak your dose based on how hard you’re training and the results you’re after. Generally, lower doses are good for everyday energy support and fat loss, while higher doses are more common during intense cutting phases.
- Administration: You can inject L-Carnitine either into your muscles (intramuscularly). Most people take it about 30-60 minutes before cardio to help boost fat burning during the workout. If you’re using it for general energy, you can take it in the morning on an empty stomach. One thing to keep in mind: it’s a good idea to switch up your injection sites to avoid irritation or scarring.
- Precautions: L-Carnitine is pretty safe overall, but some people might notice things like stomach upset or muscle cramps, especially with higher doses. To avoid these, make sure you’re staying hydrated and slowly increase your dose if needed.
Side Effects
Here are some possible side effects to keep in mind with L-Carnitine:
- Nausea
- Digestive issues like diarrhea or cramping
- Reactions at the injection site (redness, swelling, or discomfort)
- Muscle cramps
- Headaches
- A fishy body odor (caused by a metabolic byproduct called trimethylamine)
- Seizures (for those with a history of epilepsy)
How to Store L-Carnitine
- Keep it out of reach of children
- Store it in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight
- Room temperature storage is ideal
- Don’t use it past the expiration date


